The Psychology Behind Laughter: How Humor Affects the Brain
Understanding the psychology behind laughter provides fascinating insights into how humor affects the brain. Laughter is a complex psychological response that involves various regions of the brain working together. When we encounter something funny, our brains quickly process the information, leading to a series of cognitive and emotional reactions. The brain’s limbic system, responsible for emotions, plays a crucial role in processing humor. Additionally, the neocortex, involved in higher-order thinking, helps us comprehend the joke and find it amusing.
Research has shown that laughter triggers the release of endorphins, neurotransmitters that promote feelings of pleasure and reward. This neurochemical response not only enhances our mood but also reduces stress and anxiety. Furthermore, studies have indicated that humor can improve memory and learning by stimulating multiple areas of the brain and increasing neural connectivity. The psychological impact of laughter extends beyond the immediate experience, contributing to overall well-being and mental health.
In conclusion, the psychology behind laughter reveals the intricate ways in which humor affects the brain. Understanding the underlying mechanisms can provide valuable insights into the cognitive and emotional aspects of human behavior, and highlight the importance of incorporating laughter and humor into our lives for mental and emotional well-being.
The Physiology of Laughter: Exploring the Body’s Response to Humor
Laughter is a universal language that transcends cultural boundaries and connects people in moments of joy and amusement. Behind the seemingly simple act of laughter lies a complex physiological response that reflects the intricate workings of the human body. Understanding the physiology of laughter provides valuable insights into how humor impacts our physical and mental well-being.
When we encounter something humorous, whether it’s a witty joke or a comical situation, the brain initiates a series of neurochemical events. The frontal lobe, the area associated with reasoning and decision-making, plays a significant role in processing the stimuli and determining its humorous nature. As the brain recognizes the humor, it triggers the release of feel-good neurotransmitters, such as dopamine, which contribute to the sense of pleasure and reward.
Simultaneously, the brain sends signals to the facial muscles, prompting them to contract and produce the characteristic sound of laughter. This physical response involves the activation of the zygomatic major muscles around the mouth and the orbicularis oculi muscles around the eyes, resulting in the familiar expression of amusement. The act of laughter also stimulates the release of endorphins, natural painkillers that can induce a sense of euphoria and relieve stress.
Moreover, laughter has been found to have positive effects on the cardiovascular system. It can lead to the expansion of blood vessels, allowing for better circulation and potentially reducing blood pressure. Additionally, laughter is believed to enhance immune function by increasing the production of immune cells and antibodies, thus bolstering the body’s defense mechanisms.
Research into the physiology of laughter has emphasized its role in promoting overall well-being, from its effects on mood regulation to its potential stress-reducing properties. By delving into the body’s response to humor, scientists continue to uncover the intricate connections between laughter and health, highlighting the profound impact of a simple smile or a hearty chuckle on our physiological functioning.
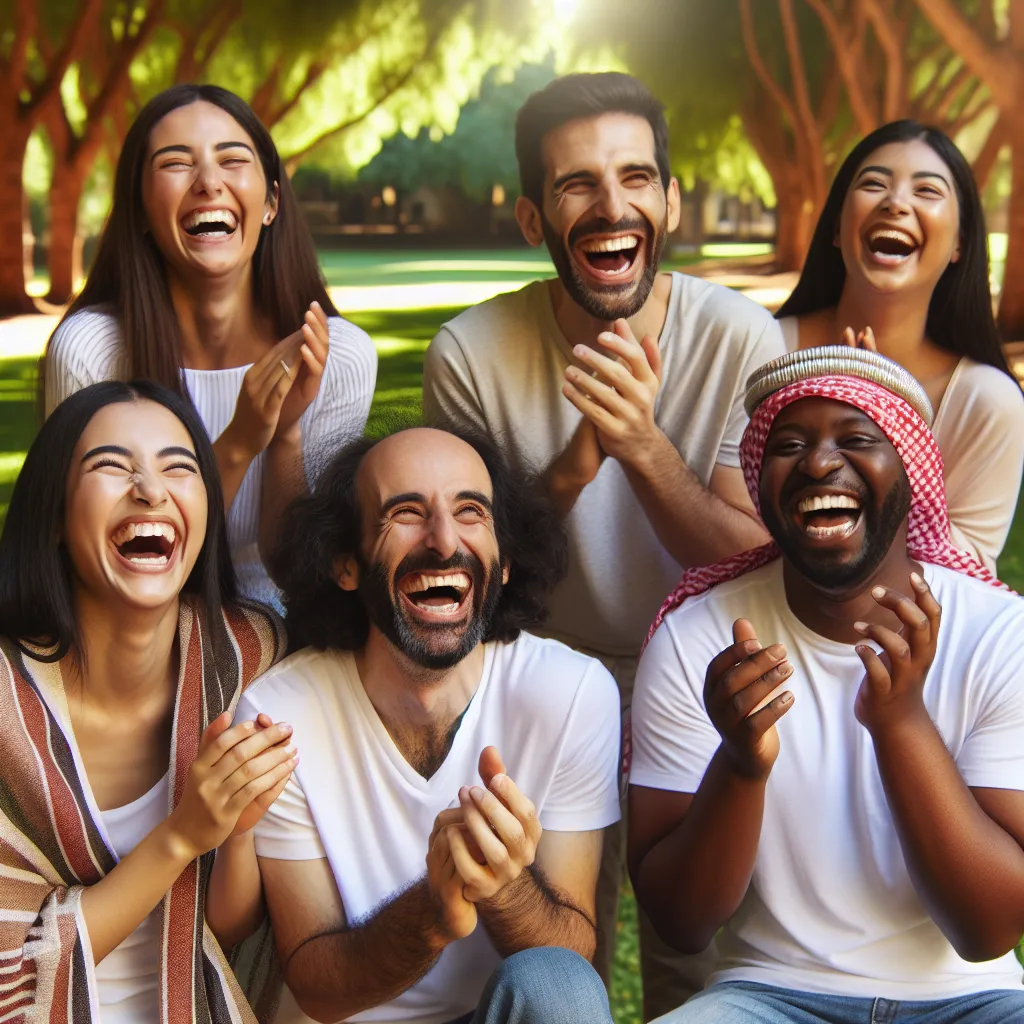
The Social Impact of Laughter: Why Laughter Is Contagious
Laughter is a universal language that transcends cultural and linguistic barriers. Its contagious nature has been a subject of fascination for scientists and psychologists alike. Research has shown that the sound of laughter can trigger the same response in our brains as when we actually laugh ourselves. This phenomenon, known as “laugh contagion,” is a powerful social force that brings people together and strengthens social bonds. When we hear someone laughing, it’s hard not to join in, even if we don’t know what the laughter is about.
Studies have demonstrated that the contagiousness of laughter is deeply rooted in our evolutionary past. Laughter served as a way for our early ancestors to communicate safety and reassurance within social groups. In today’s world, the ability of laughter to spread rapidly through a group can still be observed, whether it’s at a comedy club, in the workplace, or even in the form of viral internet memes.
Furthermore, laughter has been found to have a profound impact on our social interactions. It can diffuse tension, ease conflicts, and foster a sense of unity among people. In fact, research indicates that shared laughter within a group can lead to increased trust and cooperation among its members. This has important implications for various social settings, from classrooms to corporate boardrooms.
Understanding the contagious nature of laughter not only sheds light on the complexities of human social behavior, but also offers insights into how we can use laughter to enhance relationships and create a more harmonious society.